Give this list of project management terms to your trainees and rest easy. It defines key concepts and acronyms used by project managers.
A
- Activity – An activity is an element of the total project that needs to be executed in order to see the project through to successful completion. In general an activity has a desired outcome, expected time duration for completion, a list of resource requirement and a pool of talent allocated to it.
- Activity Delay – The maximum allowable, tolerable delay in reaching the dead line of a particular activity due to lack of resources is termed as “Activity Delay”.
- Activity Splitting – The act of splitting up a particular activity into segments and then allocating resources to these segments is a popular concept in preemptive project management. In this way resources are sometimes freed up which can be dedicated to other activities. In this approach, the requirements of the activity are more practical than estimated because the nuts and bolts of the activity have already been analyzed.
- Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP) – This is a very important concept especially for large organizations. It can become the difference between the success and failure of a particular project. Actual Cost of Work Performed is the total cost incurred to see the work to completion and includes both direct costs that are generally accounted for and the more elusive indirect costs which are not included in the final costing sheet.
- Agile Project Management – This is a relatively novel approach to project management which borrows heavily from the tenets of agile software development. The baseline objectives are to ensure complete involvement of stakeholders, an iterative work methodology, teamwork and effective controls so that the execution of a project proceeds in an agile (fast) yet efficient way.
- Allocation – The process of dispensing available resources to projects in an economic way so that each activity can be completed on time.
- Aggregate Planning – This is a predictive operational process with the help of which stakeholders estimate the quantity of resources required to complete the project successfully. These are procured at least 8 to 12 months in advance in order to ensure both quality and the most economic deals.
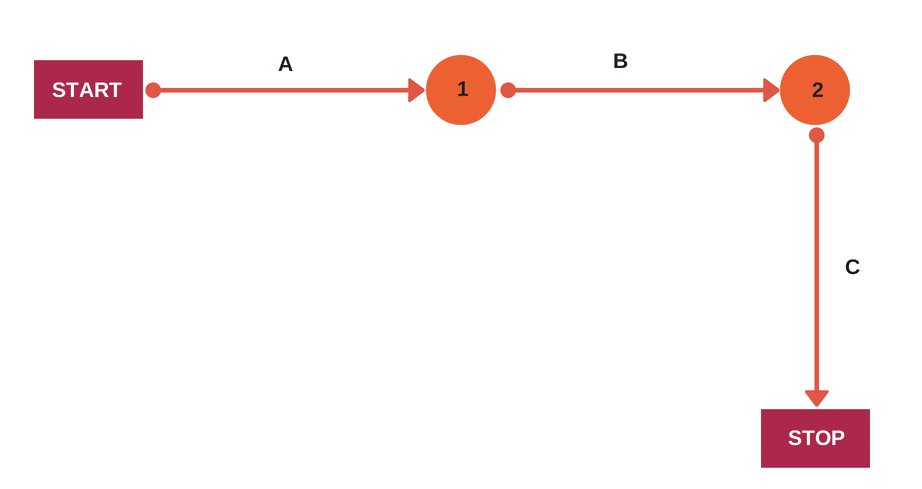
- Arrow – The visual or diagrammatic representation of an activity is termed as an arrow.
- Arrow Diagramming Method – This is a method with which a complex project comprised of several activities and a tight schedule can be represented visually or diagrammatically. Each activity is represented by an arrow where the start of the arrow is the scheduled starting date of the activity and the end of the arrow is the ending date of the activity. These arrows meet at nodes denoted by small circles and help to keep track of the sequence in which the activities should be performed.
- Assumptions – These are factors supposed to be in place to contribute to the successful completion of a project. Assumptions may or may not be validated by proof.
B
- Backward Pass – The process of calculating the Late Start and Late Finish dates of the uncompleted portions of all network related activities.
- Baseline – It is a minimum or basic execution plan for a project complete with starting and ending dates as well as financial calculations around the project. The baseline as the name suggests is the foundation upon which the project grows. It is flexible and is expected to change with time and changing project and Enterprise needs.
- Baseline Schedule – It is rudimentary schedule consisting of baseline start and finish dates subject to changes in future depending upon internal and external factors influencing the project.
- Budget – It refers to a sheet of planned expenses and revenues for a particular project. It is one of the foundations based upon which the future course of projects is determined.
- Budgeted Cost of Work Performed – This is the sum total of all the approved expenses for activities or portions of an activity actually performed till date. It includes overhead costs as well.
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled – This is the sum total of all related expenses (including overheads) of activities scheduled to be performed over a given time period.
- Business Analysis – It is the compendium of knowledge, tools and techniques required to identify business needs, problems and tailored solutions to these problems. Business data analysis is a closely aligned concept with the help of which “big data” generated by the organization is crunched to reveal insights about growth and performance.
- Business Case – It is a succinct document outlining the motives behind initiating a particular project, the financial calculations regarding the project and the justification of the vision the project needs to strive towards.
- Business Model – A business model is a system geared to produce profits consistently for an organization based upon a plan for resource procurement, customer base identification and other details of financing.
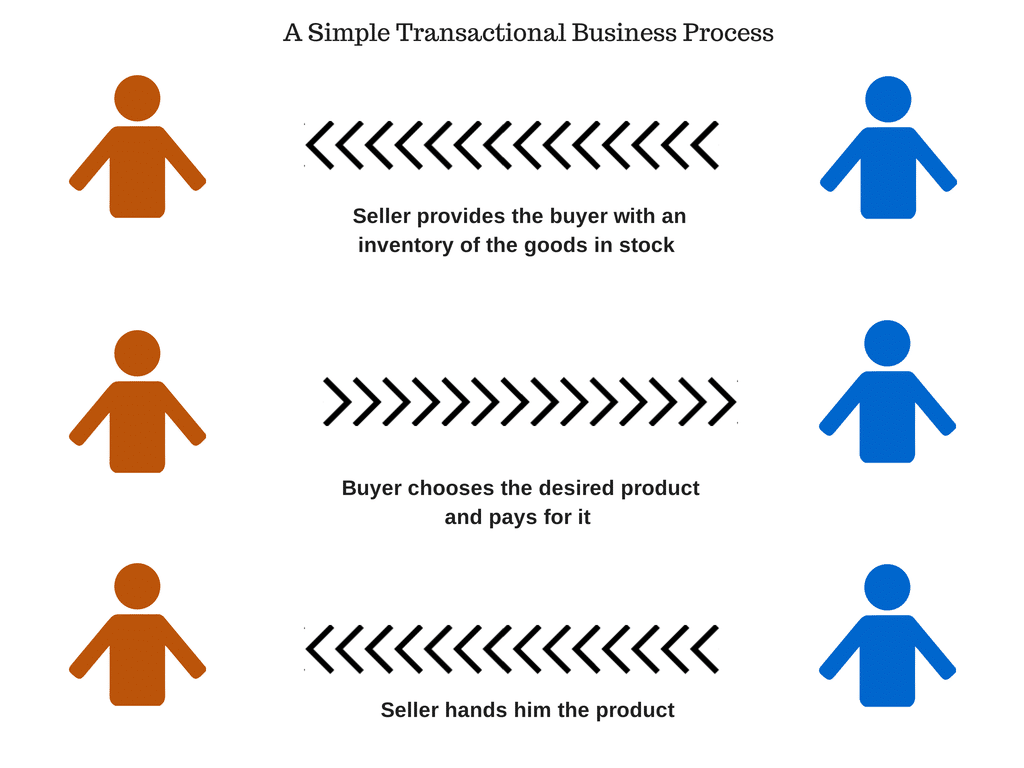
- Business Process – A business process is a collection of related, ordered and inter-dependent activities and tasks which yields and facilitates distribution of a finished final product for a particular customer base. In the real life scenario, a business process may be a vendor selling a product to a customer as depicted below.
- Business Process Modeling – BPM is the representation of a process in its original form so that stakeholders can analyze its impact within a project and tweak it to boost performance where necessary.
C
- Capability Maturity Model (CMM) – This is a software development model defined by SEI. It is used to describe the maturity of the capabilities of business processes over the 5 distinct levels initial, repeatable, defined, managed and optimizing.
- Case Study – A case study is defined as a systematic way of scrutinizing an event and noting the factors behind its initiation, its results, its impact, the insights that can be gleaned from it and a wealth of other information.
- Change Control – Change Control refers to the assembly of techniques and measures with the help of which change is introduced within a system in a coordinated manner so that its effects can be monitored and analyzed. Addition of features to a project under development can also trigger changes to the existing foundation of work.
- Change Management – It is a branch of management that is largely dependent upon change control. It is a compendium of tools, measures and techniques with the help of which change (either deliberate or involuntary) can be monitored to ensure maximum performance of the system.
- Constraints – These are defined as influencing factors you must consider or take into account throughout the lifetime of a project. Constraints may be deadlines, resource unavailability, and regulatory requirements.
- Construction – It refers to the process of building or creating a final product, generally tangible in nature. Construction is rarely a simple concept. It comprises of multiple activities in a logical sequence to ensure that the final product complies with quality guideline specifications.
- Cost – In the sense of project management costs refer to the amount of liquid cash spent in either acquiring an asset or creating a product such that the resource is no longer available for investment in other avenues.
- Cost Benefit Analysis – This is an important project management tool which uses monetary units to justify the initiation of a project. With the help of this analysis project managers can convince stakeholders that the ultimate profit or pay off is worth the investment and the associated risks (if any)
- Cost Overrun – It is defined as expenses over and above the budgeted or approved expenditure in order to complete a project. For project management to be effective, this value should be as close to zero as possible.
- Cost Performance Index (CPI) – It is the ratio of the budgeted costs to the actual costs. It is an indication of the cost overrun of the project.
- Cost Variance – Cost variance is defined as any appreciable difference in the estimated cost of an activity and the actual cost of undertaking or completing the activity.
- Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) – This is a technique that focuses on the resources needed to complete the activities within a project. Thus it mainly deals with the constraints introduced into the project because of unavailability or limited nature of resources.
- Critical Path – The critical path is the longest, logical sequence of activities connecting the initiation to the termination. Each activity along the critical path must be completed on time in order for the project to adhere to its schedule.
- Critical Path Method (CPM) – It is a tool used to predict the schedule of a project by identifying the logical sequence of activities with the least flexibility in terms of deadlines.
D
- Deliverable – A deliverable is a tangible document, hardware or product that has to be created as per the contract and in adherence to specified quality, state and process guidelines within a given time duration and budget.
- Dependency – Within a project dependency refers to the link or interrelatedness of activities with one another such that it can affect the final outcome of the project. Dependencies within a project tend to make it more complicated because the processes applied to one activity may as well have far reaching repercussions on other dependent activities.
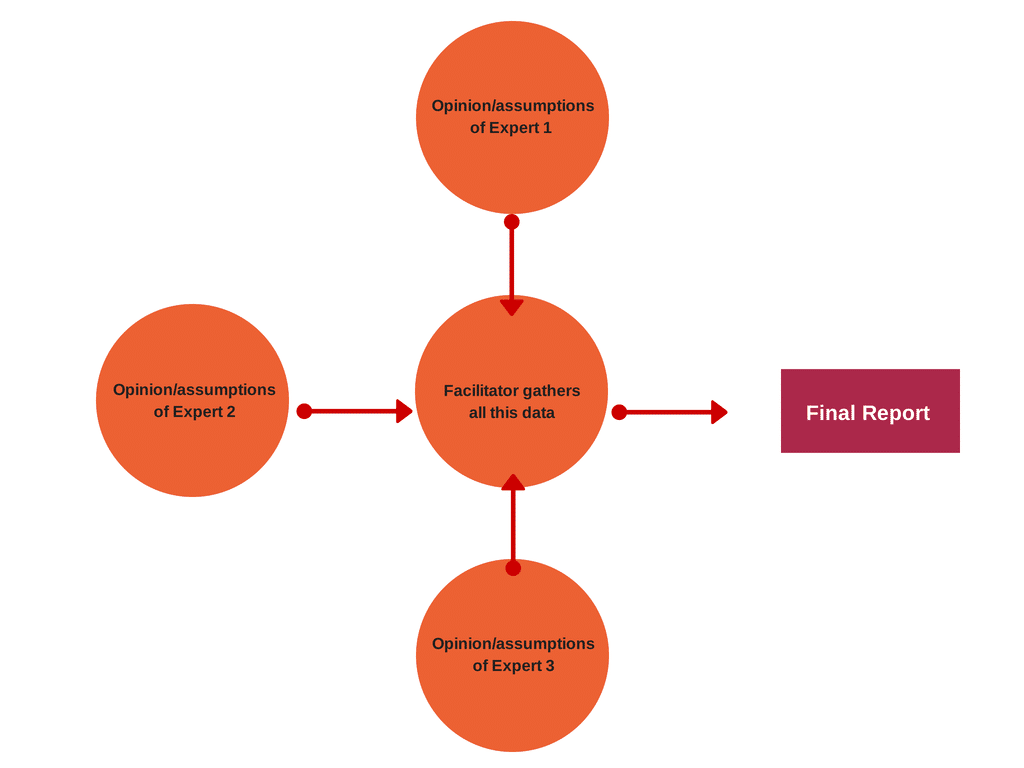
- Delphi Technique – The Delphi Method is a structured, predictive communication method which looks to reach a general consensus on a debatable topic where factual data provides inconclusive results. This technique leverages the power of expert opinion which is summarized by a facilitator in the form of a final report.
- Duration – The number of units of work period required to see an activity through to successful completion. These work units may be days, hours or months.
- Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) – DSDM is a simple, extensible agile framework which is generally used in the domain of software development. It focuses on continuous user involvement and with its incremental approach is thought to introduce a level of discipline in agile processes.
E
-
- Early Finish (EF) Date- Within the Critical Path Method, Early Finish Date refers to the earliest possible time by which the uncompleted portions of an activity on a smaller scale or a project on a larger scale can be completed, keeping in mind the various schedule constraints and the logic of the process flow.
- Early Start (ES) Date – Within the Critical Path Method, Early Stat Date refers to the earliest possible time by which the unfinished portions of an activity or project can be tackled for completion, paying heed to the various constraints related to the endeavor.
- Earned Value – Earned Value (EV) is a project performance monitoring guideline that compares the actual work required to the work accomplished in order to gauge whether the progress of the project is on schedule or not. It is also a representation of how well the budget (finances, talent and other resources) are being utilized to aid the completion of the project.
- Earned Value Management – The EVM system is basically used to integrate scope, schedule and cost of the project in a single system to monitor project progress in an objective manner.
- Effort – The number of labor units required to complete a particular activity is termed as effort. It can be measured in terms of staff-weeks, man-hours and so on.
- Effort Management – This is a sub discipline of project management that deals with the most efficient possible use and direction of the available resources and their expended effort to ensure that the final project deliverables comply with the quality, timeline and the budget of the contract.
- Enterprise Modeling – It is defined as an abstract representation of the relevant business domain, business processes and information technology growth of an organization or company to ultimately improve its overall performance.
- Estimate at Completion (EAC) – EAC refers to the estimated total cost of an activity or a project to the organization as defined by the complete scope of work.
- Estimation – In project management it refers to the process of making an accurate assumption about the final state of either a costs tally or some similar tangible business aspect using appropriate methods to eliminate error.
- Event Chain Diagram – It is a diagrammatic representation of the interrelationship between events and tasks and how they affect each other.
- Extreme Project Management – It is the process of managing a project that is very complicated and likely has uncertain outcomes.
F
- Focused Improvement – It is the assembly of activities with the help of which the performance of a particular activity can be improved by systematically eliminating all constraints. It works on the principles of the Theory of Constraints and is basically applied to manufacturing.
- Float – It is the net duration of time by which an activity completion can be delayed without adversely affecting the subsequent activities or the project completion date on the whole.
- Forward Pass – The process of calculating the Early Start Date and the Early Finish Date of the uncompleted portions of all network activities.
- Free Float – It is the net duration of time by which the completion of an activity can be delayed without affecting the early start date of the next activity.
G
-
- Gantt Chart – The Gantt Chart is a type of bar chart invented by American engineer Henry Gantt in 1910. It is a graphic representation of the schedule of a project (start and finish dates of the terminal elements and the summary elements of a project) thereby breaking down the work process into smaller components for easier analysis.
-
- Goal – A goal represents the desired/projected state of affairs of a particular enterprise (high level) or activity (low scale) towards which all stakeholders should strive in order to attain success. Generally goals are associated with a timeline that has to be adhered to.
-
- Goal Setting – The logical process of selecting specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and timed goals is termed as Goal setting.
-
- Graphical Evaluation & Review Technique (GERT) – It is a network analysis technique that allows for conditional and probabilistic treatment of network logic and the activities processed through this logic. In GERT deterministic branching plays an important role because events taking place as a result of the initiating event are all assigned separate probabilities and tackled one at a time. It is not as important as PERT.
H
-
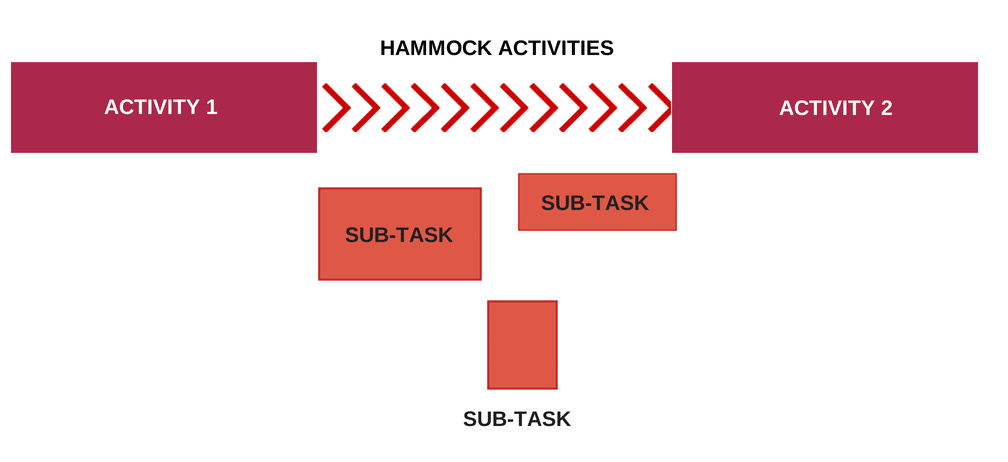
- Hammock Activity – It is a project management term that is used to refer to an aggregate of sub-tasks which are not really related to one another but must be accomplished before the starting date of the next activity in order to achieve the desired goal. These activities can be executed in a random sequence.
- Holiday – A defined timeframe within the project schedule when activities can’t be initiated.
I
- Integrated Master Plan (IMP) – This top level plan consists of the hierarchy of all the program events within a project. Here each event is associated with a specific objective that must be achieved in accordance with the criteria of its achievement.
- ISO 10006 – This is a standard developed by the International Organization for Standards (ISO) to govern project management.
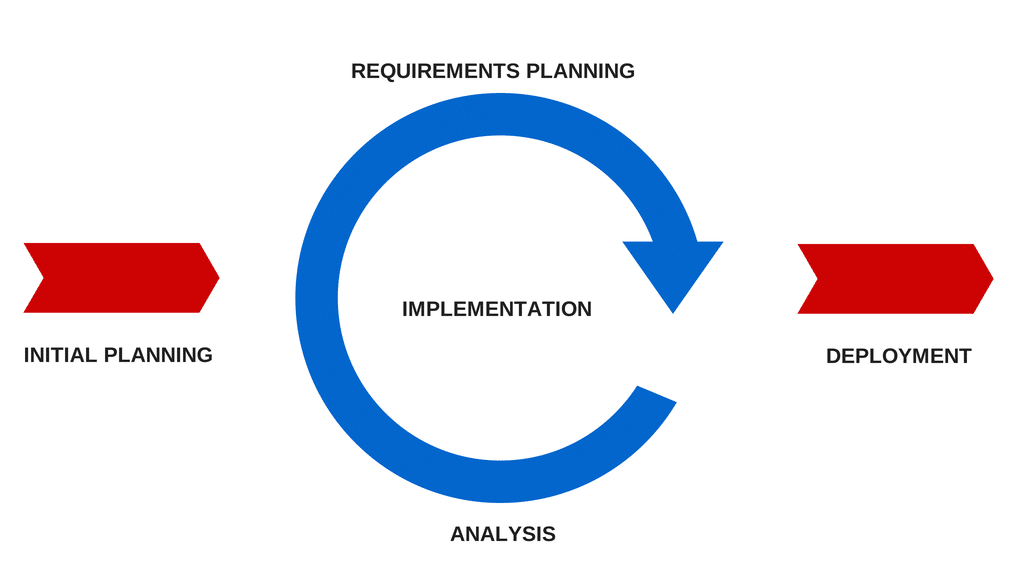
- Iterative and Incremental development – This is a software development process of long standing that leverages both incremental and iterative approaches. The features are added in increments and the upgrade pattern is cyclical. Thus there is cyclic interaction between initiation and deployment dates.
K
- Kickoff Meeting – This is the crucial first meeting between the client and the execution team prior to starting work on the project. Important decisions are taken at this meeting. Guidelines are set and the chain of communication established.
L
- Lag – A logical relationship modification within a network which directs a delay towards the succeeding task.
- Late Finish Date – According to the Critical Path Method, the Late Finish Date is the latest possible time at which an activity can be completed without delaying the succeeding activity.
- Late Start Date – According to the Critical Path Method, the Late Start Date is the latest possible time at which an activity can start without delaying the succeeding activity.
- Lead– A simple modification to the logical relationship within a network that results in the acceleration of the succeeding activity. For example if a finish to start project has a 10 day lead, the successor task can start 10 days before the preceding task has ended.
- Lean Manufacturing – Lean Manufacturing is a framework geared to cut down production costs. It views any expenditure that is not a part of the value creation process for the presumed client a waste and thus is ear-marked for elimination.
- Logic– A complete collection of the inter-dependencies between projects to define the project network diagram.
- Logic Network – The diagrammatic representation of the sequence of activities within a project is known as a Logic Network. The logic network is responsible for establishing the sequence of the activities – that is which activity should logically succeed another and which activity should precede it. A project manager can identify milestones and the critical path through this network.
- Loop – A loop is a GERT provision which shows a network path or deterministic branch that passes through the same node twice.
M
-
- Management – Management is a discipline involving organization, recruitment, control and guidance of a group of people and other tangible resources in order to complete a goal or reach a collective vision. It has importance in both the business and social settings.
- Management Process – It is the process of controlling any activity or event so that risks are minimized and the resources are leveraged to the optimum extent in order to produce great results.
- Management Science– It is a mathematical-analytical model which is implemented to help project managers and stakeholders reach more informed business decisions.
- Maximum number of Segments – The maximum number of smaller units into which an activity can be divided.
- Mega Project – It is an investment project on an extremely large scale. A mega project in general costs more than a billion USD and has profound impact on people, environment or the economy.
- Milestone – A milestone is an important noteworthy event over the lifetime of a project, especially pertaining to deliverables.
- Monte Carlo Simulations – These simulations help stakeholders see all possible outcomes and the respective probabilities of a complex project or activity. They help gauge the sensitivity of a system under conditions of statistical constraints and are popular risk assessment tools.
- Motivation – The driving set of psychological reasons leading to a particular behavior or activity.
- Murphy’s Law – It is an important law which is said to keep project managers on their toes. It states that “If anything can go wrong, it will”.
N
-
- Net Present Value (NVP) – This is a predictive tool that allows organizations to calculate the worth of long term slow yielding projects. It compares the present value of a unit of the currency against the future value of the same unit after taking into account inflation and other influencing factors.
- Network Diagram – It is the chronological, schematic representation of the logical relationships of all project activities.
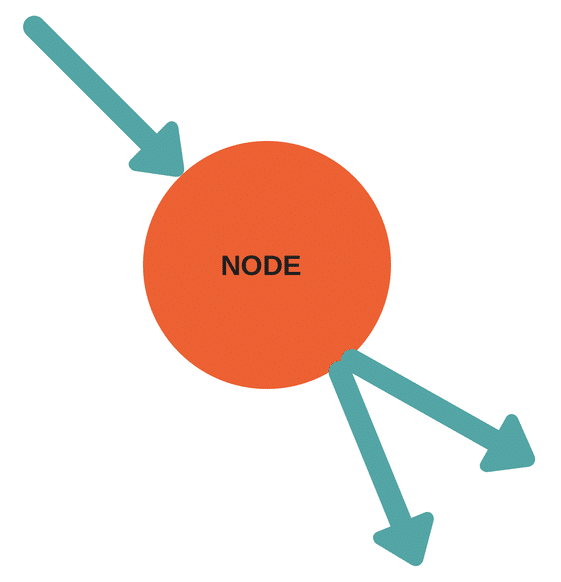
- Node – A node is a critical defining point within a network where dependent activities converge or diverge from.
- Non-Linear Management – This approach takes into account the changing nature of the business landscape and allows organizations to adapt their existing strategies to yield better results. It seeks to develop order and encourages businesses to embrace evolutionary, lean and agile methodologies.
O
- Operations Management – The department of the business that is in charge of producing high quality goods and services. It also facilitates distribution of the goods and services.
- Organization – This is an aggregate of resources tangible, human and intangible which is well defined and separate from its environment. An organization has social impact and a set of goals which it strives towards.
- Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS) – This is a hierarchical model which relates work packages to organizational units. It thus establishes the framework for resource allocation; time and schedule management and most importantly work management.
- Organization Development (OD) – The well-structured methodology which governs the growth, expansion and diversification of an organization in keeping with industry norms and enterprise vision.
P
-
- Pareto’s Principle – This principle postulated by Vilfredo Pareto states that 80% of the benefit of a project can be achieved by completing only 20% of the tasks. It is one of the basic tenets of time management and introduces the concept of working smarter rather than harder.
- Path – A path is a number of sequentially connected activities within a project network diagram.
- PERT – PERT stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique. It was developed by the US Navy in 1950 and is used to schedule, organize and manage tasks within the framework of a project. It is very similar to CPM.
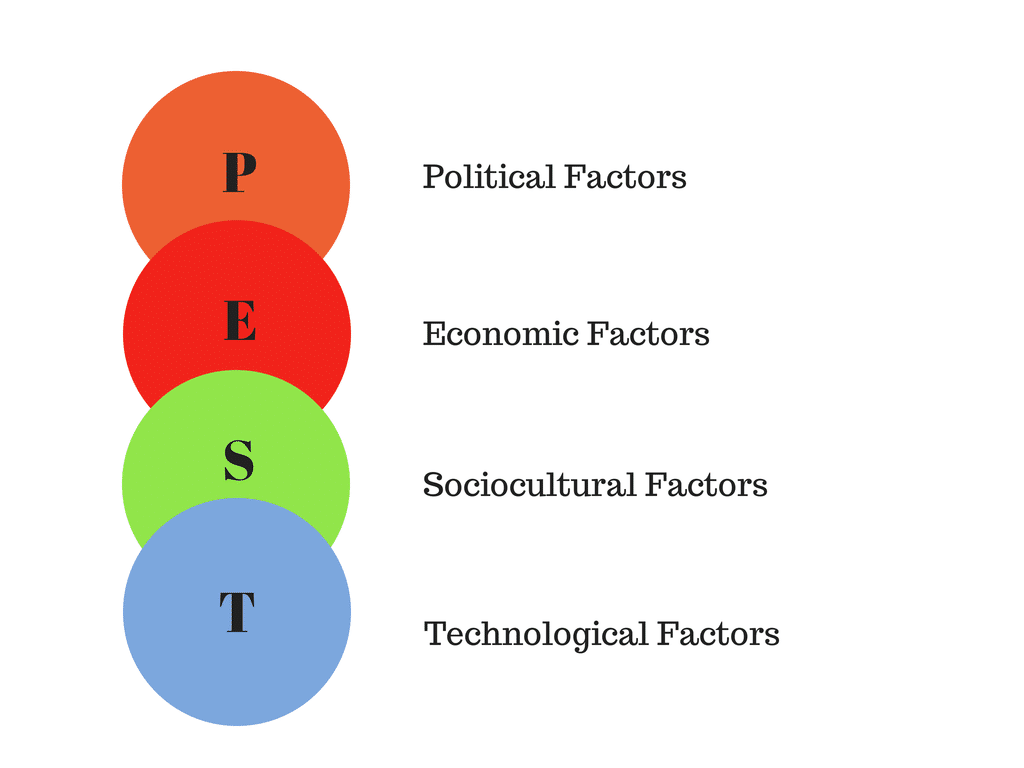
- PEST Analysis – It is a strategic planning tool with the help of which the impact of external factors like politics, environment, social sentiments and technological growth upon the outcome of a project is determined.
- Planning – Planning refers to the structured process of creating a plan after thinking through in detail the impact and the sequence of the activities involved.
- Portfolio – It is the dossier of investments and acquisitions in the name of an individual. In terms of an organization it refers to the cross functional-inter-departmental selection of projects which need to be executed in order to further the organization along its road to goal achievement.
- Project – A project is a methodical, planned undertaking which is comprised of a selection of logically related activities. Its ultimate objective is to produce a final deliverable of high quality.
- Project Management – It refers to the set of tools, techniques and processes with the help of which the course of execution of a project is managed for optimum results.
- Project Management Office (PMO) – is a specific department within an organization that is responsible for maintaining the standards of project management within that organization.
- Project Management Triangle – The project management triangle is a model that explains how the three constraints of scope, schedule and cost affect the ultimate quality of the final product or deliverable.
- Project Plan – A project plan is defined as a document which is used to keep track of deliverables, deadlines, processes and process requirements, the basics of sound communication between the stakeholders and most importantly the baselines values of KPIs in comparison to the desired values of those same KPIs. A project can’t attain its desired objectives without the proper guidance of its project plan.
- PRINCE2 – PRINCE2 is a generic project management methodology which is used to monitor all aspects of the process of execution and the motivations of the people involved so that the final deliverable is high quality and economical. It also has provisions for tweaking an ongoing project if it doesn’t develop as planned.
- Process – A process is a collection of logical activities in a given sequence so that inputs may be converted to the desired outputs maintaining high quality and specification compliance.
- Process Management – The ensemble of activities associated with monitoring various processes critical to the execution of a project is called Process Management.
- Product – It is any tangible object which can offer value to its buyers in exchange of monetary compensation to the seller.
- Product Breakdown Structure – It is a product based planning technique which serves as a tool for breaking down, analyzing and communicating the outcomes of a project.
- Product Description – It is the formal document responsible for providing all the specifications of a product.
- Project Management simulators – These are computer based project management tools that simulate group activities which require participants to either hone their existing skills or assimilate new techniques as a part of a learning experience.
- Project Network – A project network is the graphical representation of the end elements and dependencies of the project. It is also indicative of the sequence in which activities need to be executed to ensure successful completion of the project.
- Project Portfolio Management (PPM) – It is the technique with the help of which the dossier of projects selected by the organization are undertaken, guided and managed in order to yield maximum results after risk mitigation.
Q
- Quality – In the manufacturing and project management domain, quality refers to the non-inferiority or the aptness or degree of relevance of the outcome of a particular activity or project.
- Quality, Cost, Delivery (QCD) Analysis – This analysis is important because it scrutinizes an activity and its performance on the basis of the three said parameters and also develops new KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) which can further help assess the success or failure of the activity.
R
-
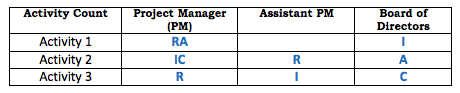
- RACI (Responsible-Accountable-Consulted-Informed) Chart – The RACI chart is an important matrix where the dimensions are the actions undertaken or activities and the people in authority positions within the organization. When an action and a person intersect, that particular action becomes the direct or indirect responsibility of the person concerned. Additional information in the form of the person to be informed after the execution of the action, the person to be consulted before undertaking the action and the person to be held accountable can also be derived from the RACI chart.
- RAID Log – A simple log which can track the risks-assumptions-issues-dependencies related to activities within a project.
- Resource – Resources are the essentials with which a project reaches completion. They can run the gamut from people to technologies to strategies to hardware and software.
- Resource Constraint Scheduling – It is a scheduling methodology which takes into account the various constraints around available resources before scheduling activities and milestones within a project.
- Resource Leveling – A special kind of network analysis in which scheduling decisions (like start and end date) are influenced by the availability of the resources, the elusiveness of certain resources and other resource management concerns.
- Risk- It is the probability with which an undesirable event may transpire.
- Risk Management – It is the specialized branch of project management with the help of which the various risks associated with the execution and the outcome of a particular project are gauged and then minimized.
- Risk Register – A tool commonly used in risk management with acts as a central database for the various identified risks associated with a project. It also catalogues risk probability, mitigation measures and impact.
S
-
- Schedule– A schedule is defined as a register of a projects terminal elements and their start and finish dates.
- Schedule Performance Index (SPI) – Simply put it is the ratio of work performed to work scheduled. It is an indication of project time overrun.
- Schedule Variance – It is the difference between the scheduled completion date of an activity and the actual completion date of the same activity.
- Scope– Scope is the sum total of all the features and requirements of a product or project deliverable. The scope of a project has to be realistic and aligned with the availability of resources.
- Scope Creep – If a project isn’t properly defined to begin with, there might be last minute, unavoidable changes to the scope of a project. This is termed as scope creep.
- SCRUM – It is an agile, iterative, incremental software development process that can be parlayed into project management terms. It consists of SCRUM masters, development teams and product owners.
- Six Sigma – Six Sigma is a project management methodology in which desired results from the outcome of a project are determined in relation to industry standards and the baseline values of project KPIs. It involves the following steps: Define Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control often referred to as DMAIC.
- Sponsor – A sponsor is an authority figure who either provides the finances for the project or has the final say in all financial matters.
- Sprint – A sprint is defined as an iterative unit of time and is a concept that is prevalent in agile project management circles. Working in sprints not only ensures elevated productivity without disruptions, it also ensures periodic reviews so that the progress can be assessed accordingly.
- Stakeholder – A stakeholder is an authority figure who is affected by the outcome of the project or deliverable. Clients, directors, investors are all key stakeholders.
- Statement of Work (SOW) – It is a comprehensive description of all the possible work that must be accomplished in order to complete a particular project. It is compiled once and is treated as the bible for the project.
- Sub-task – An activity or task contained within a super-task.
- Super task – An aggregate of activities or sub-tasks is termed as a super-task.
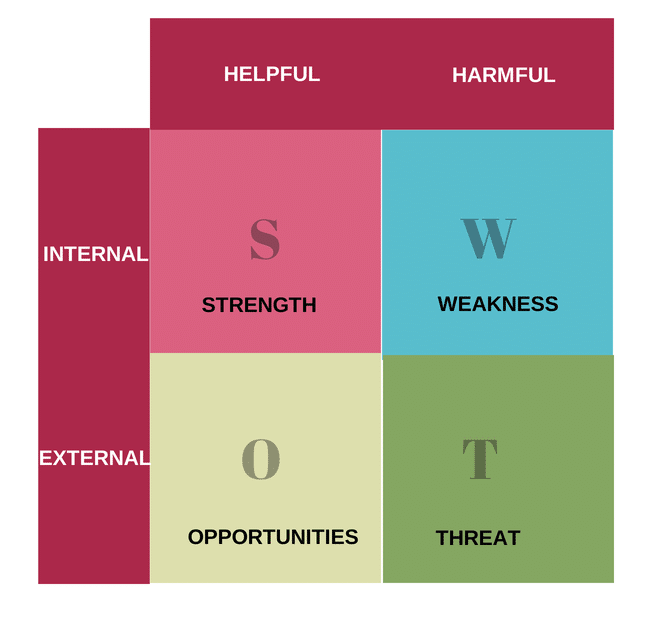
- SWOT Analysis – It is a market research tool that is invaluable to businesses either launching a new product or trying to break into a new market. It helps create a matrix of the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of the business in question under the given circumstances.
- Systems Development Lifecycle – It is the logical process of development of an information system that adheres to the requirements of the client and exceeds expectations within the given timeline and budget.
T
- Target Date – A target date is defined as an alignment constraint which is used to restrict and freeze the start or finish date of a project or activity.
- Task– A set of defined actions which can lead to the completion of job or a problem.
- Task Analysis – It is the breakdown of a task or activity from the timeline so that it can be scrutinized in terms of resources required for completion, its impact and other considerations.
- Theory of Constraints (TOC) – Theory of Constraints is an important management philosophy which identifies the most important constraint within a project framework and improves all activities to either eliminate the constraint or work around it.
- Timeline – A timeline or chronology is the graphical representation of the logical sequence of events or activities to lead a project to completion.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – TCO refers to all costs direct or indirect incurred in the acquisition and maintenance of an asset over a lifetime.
U
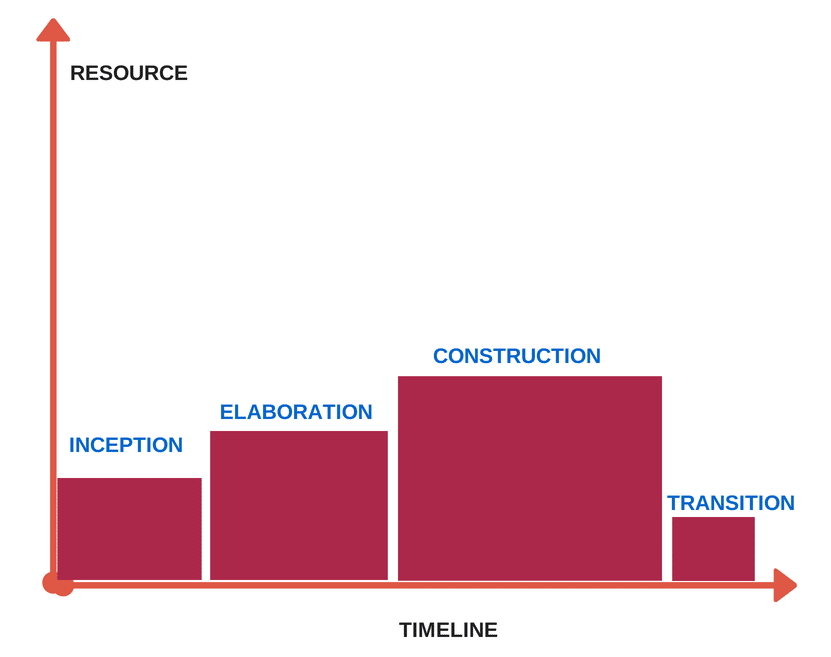
- Unified Process – This is a famous extensible iterative and incremental development framework that can be customized to suit different organizations. It is use case driven and divides the development process into four distinct phases – Inception, Elaboration, Conception and Transition.
- Use Case – Use Case is used to define the specification of tests conducted keeping in mind the end user experience.
V
- Vertical Slice (VS) – It is a type of milestone which is used to indicate and gauge progress across all layers of a particular project. It is a staple of the SCRUM methodology.
- Virtual Design and Construction – It is termed as the management of integrated, interdisciplinary performance models so that they can be tweaked to achieve specific business and social objectives.
W
-
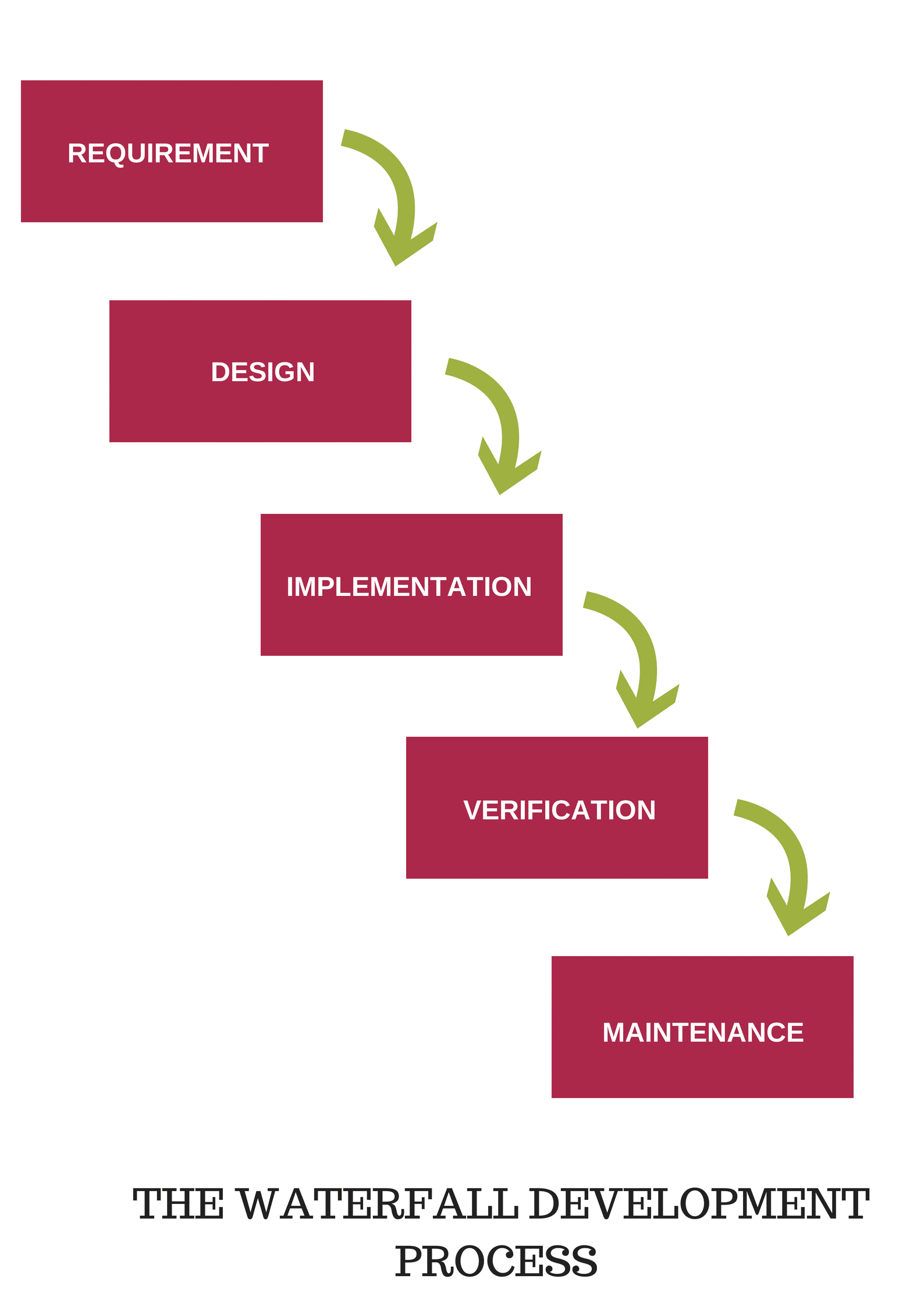
- Waterfall Model – It is a development model in which progress is always downwards like a waterfall and there are no overlapping or iterative steps. The sequential flow of progress goes through the phases Conception, Initiation, Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production/Implementation, and Maintenance.
- Wideband Delphi – It is a widely used forecasting tool that derives from the Delphi Method to reach a final consensus regarding issues of import. It is termed “wideband” because in comparison to the Delphi Method, there is greater interaction and communication between the participants.
- Work – Work is referred to as the amount of effort that must be expended in order to accomplish a particular end goal.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) – The WBS methodology or grouping defines the scope of the total project. It is a chart in which the critical tasks are illustrated to display their interrelationship and the relationship to the project as a whole. It is a top down approach where with each descending level, an increasingly detailed definition of the project components can be accessed.
- Work Packages – Deliverables at the lowest level of the WBS. Work packages are comprised of activities.
- Work Shift – Work shift comprises of pairs of on/off working times that can be considered together to define the working day.